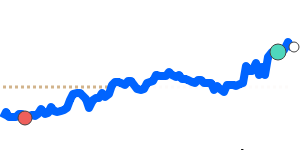
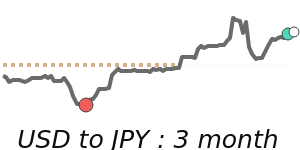
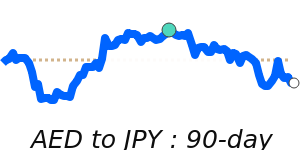
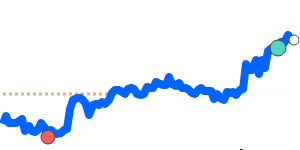
The Japanese yen remains somewhat subdued against the US dollar, trading approximately 1.1% below its three-month average. Recent monetary policy changes by the Bank of Japan, including ending negative interest rates and raising the benchmark rate to 0.5%, have influenced sentiment, but the yen hasn't gained significant strength yet.
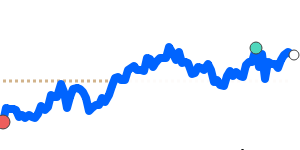
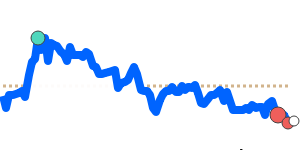
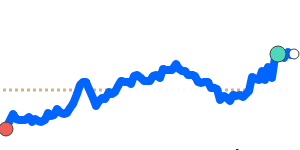
against the Euro, the yen has held steady near its three-month average, reflecting recent stability in the EUR/JPY exchange rate. However, the yen has weakened slightly against the British pound, reaching near recent seven-day lows, below its three-month average. This recent move mirrors ongoing political and economic concerns in Japan, as well as global risk appetite fluctuations.
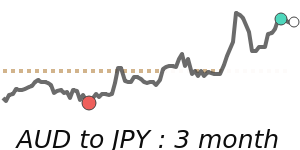
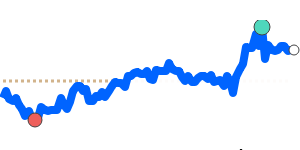
Compared to commodity currencies, the yen has seen notable declines. It is trading about 3.7% below its three-month average against the Australian dollar, with more volatility observed in recent weeks, and near its two-year lows against the Canadian dollar, roughly 2.1% below average.
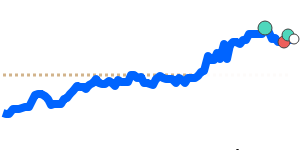
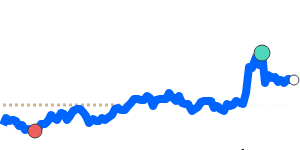
Overall, the yen's movements have been modest but reflect ongoing market concerns, including global trade tensions and Japan’s fiscal policy environment. Importers and exporters should monitor these trends, especially those involving the USD, GBP, and CAD, which have experienced more significant recent shifts.