Outlook
The Swiss franc remains supported by safe-haven demand amid ongoing geopolitical and economic uncertainty. The SNB has signaled a willingness to reintroduce negative rates if the franc stays strong, a move that could cap further CHF gains. A persistently high CHF continues to weigh on Swiss exporters and growth; if global risk appetite improves or major central banks diverge in policy, the CHF could ease modestly versus the USD, EUR and GBP.
Key drivers
- Safe-haven demand persists as a key driver for the CHF during periods of global risk-off.
- Potential SNB action: the risk of negative interest rates if the franc remains elevated, which would likely weaken the CHF.
- Exporter sensitivity: a strong CHF continues to pressure Switzerland’s tradable-sector margins and trade performance.
- Market divergence: yield and policy differentials between the Fed, ECB and SNB influence CHF moves against major rivals.
- Global risk factors: ongoing geopolitical tensions and economic instability keep CHF in demand as a stabilising currency.
Range
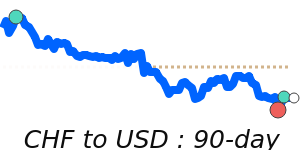
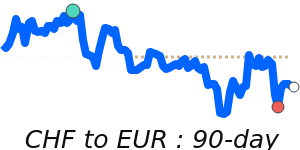
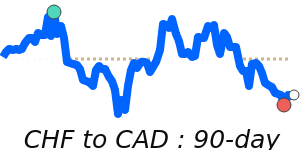
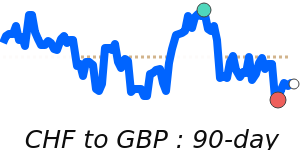
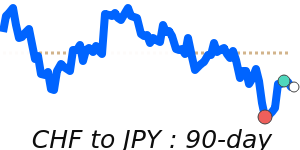
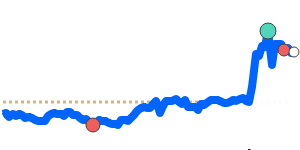
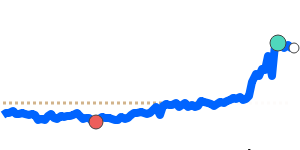
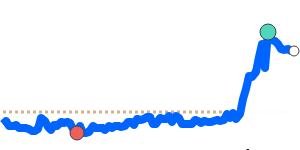
CHF/USD 1.3010 (3-month average 1.262); range 1.2350 to 1.3115 (6.2% over the range). CHF/EUR 1.0944 (3-month average 1.0778); range 1.0648 to 1.0950 (2.8% range). CHF/GBP 0.9544 (3-month average 0.9405); range 0.9298 to 0.9566 (2.9% range). CHF/JPY 201.0 (3-month average 197.2); range 193.0 to 203.4 (5.4% range).
What could change it
- SNB policy shift: reintroduction of negative rates or other tightening/loosening that alters CHF dynamics.
- Risk sentiment shifts: a move back toward risk-on or risk-off conditions affecting safe-haven flows.
- Trade and growth signals: stronger inflation or growth data in Switzerland or its trading partners, or a renewed export slowdown, could sway CHF.
- Central bank differentials: changes in Fed/ECB policy paths impacting relative yields and EUR/CHF, USD/CHF moves.