The Philippine Peso (PHP) has been on a cautious trajectory following a series of interest rate cuts by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP), most recently in August, when the benchmark interest rate was lowered to 5.0%. This reduction is part of a strategy to support economic recovery amid easing inflationary pressures; however, inflation increased to 1.5% in August, primarily due to rising costs in housing and food. Analysts note that the year-to-date average of 1.7% remains below the BSP's target, indicating a complicated inflation landscape.
Despite these measures, concerns over a persistent trade deficit—reportedly $54.21 billion in 2024—continue to apply downward pressure on the peso. The ongoing trade imbalance, coupled with a widening current account deficit, poses significant challenges for the currency's stability. Moreover, ANZ Research has highlighted that the peso's overvaluation since 2019 could impair its competitiveness, particularly in manufacturing and exports.
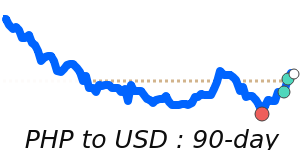
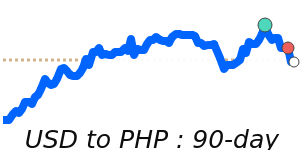
In terms of recent market performance, the PHP to USD exchange rate stands at 0.016973, reflecting a 2.1% drop from its three-month average of 0.017337, within a stable range. The PHP to EUR conversion is currently at 0.014670, 1.3% below its three-month average of 0.014857. Meanwhile, the PHP to GBP is approximately at parity with its three-month average, while the PHP to JPY is trading at 2.6061, which is 0.6% above the average. These trends suggest that the peso remains in a somewhat stable yet cautious phase, responding to both domestic monetary policy and external economic pressures.
Experts suggest that businesses and individuals engaging in international transactions should closely monitor these developments, as fluctuations in the PHP could impact costs significantly in the near future.